Nvidia (-0.17%) has consistently impressed investors with its remarkable earnings growth, which has fueled a dramatic rise in its stock price. Over the past five years, the stock has surged by 2,500%, and it’s on track for a 140% increase this year alone. The key to this performance is straightforward: Nvidia has established itself as a leader in one of the most rapidly expanding sectors today, artificial intelligence (AI). The tech giant commands an impressive 80% share of the AI chip market and provides a comprehensive array of AI products and services to its customers.
This success has translated into robust growth, enabling Nvidia to report record-breaking revenue quarter after quarter and consistently exceed analysts’ earnings expectations. This trend continued in the most recent quarter as revenue soared to $30 billion—surpassing the company’s total revenue for the entire 2023 fiscal year. The demand for Nvidia’s products remains strong, and the company is gearing up to introduce its new architecture, Blackwell, in the coming months.
However, two aspects of Nvidia’s latest report were not as positive as the rest. Should these be considered warning signs for Nvidia investors? Let’s delve deeper.

Nvidia’s GPUs
First, a brief overview of Nvidia’s journey thus far. Over the years, Nvidia has evolved from developing graphics processing units (GPUs) primarily for video games to expanding the application of these powerful chips across other industries, including AI. Today, Nvidia’s GPUs are highly sought after for critical AI tasks such as training and inferencing large language models. This has propelled the company’s earnings and stock performance, making it a favorite among technology investors.
Now, let’s examine the two elements in Nvidia’s recent earnings report that might raise concerns. While the company maintained its impressive streak of triple-digit revenue growth, the pace has decelerated compared to previous quarters. Nvidia achieved over 200% revenue growth in the three preceding quarters year over year; however, in the latest period, growth slowed to 122%. Furthermore, Nvidia’s forecast for the next quarter anticipates growth of 79% compared to the same period last year.
The second factor to consider is the company’s gross margin, which stood at approximately 75%. While this is an excellent figure, it is lower than the previous quarter’s 78.4% gross margin.
Looking at these factors in isolation, one might wonder if Nvidia’s exceptional growth is beginning to taper off. Such a slowdown could potentially impact the stock price, especially given its current valuation, with Nvidia trading at roughly 40 times forward earnings estimates.
The story behind the numbers
Before hastily deciding to sell or dismiss Nvidia, let’s explore the reasons behind the recent slower growth and reduced gross margin. Starting with revenue, it’s crucial to recognize that Nvidia is now facing increasingly challenging comparison periods. This is because we’re comparing to a time just a year ago when major customers were already heavily investing in Nvidia GPUs. Before that, AI investment was lower, providing Nvidia with more room for explosive growth.
Nevertheless, Nvidia continues to broaden its offerings, including in areas like enterprise AI, and is committed to updating its GPUs annually. These efforts should help maintain the company’s leadership position and sustain high growth levels.
Regarding the gross margin, some fluctuation is expected as Nvidia prepares to ramp up production of Blackwell. The costs associated with launching a new product and scaling up production are impacting margins at present. However, Nvidia has projected a gross margin of 75% for the upcoming quarter and around that level for the full year, which remains well above the company’s historical profit margin.
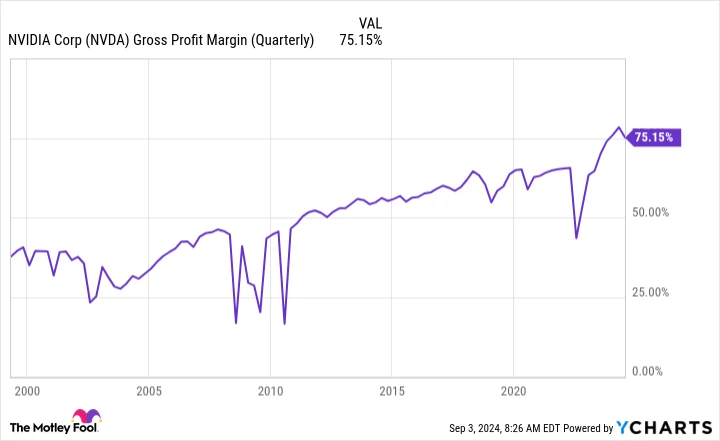
NVDA Gross Profit Margin (Quarterly) data by YCharts
Should Nvidia investors worry?
Returning to our initial question: Should Nvidia’s slowing revenue growth and lower gross margin be considered warning signs for investors? Not at all. These factors do not indicate a decline in demand or a weakening of Nvidia’s ability to profit from its products and services.
Instead, they reflect Nvidia’s current position: The company may have moved past the initial surge—when customers first began heavily investing in AI—but the growth narrative still has many chapters to unfold. Customers continue to prioritize AI investment, and Nvidia plans to launch significant new products regularly while achieving efficiency through large-scale production. All of this suggests substantial growth ahead, giving Nvidia investors ample reason for optimism.