Inflation is the overall increase in the cost of products and services. The U.S. Federal Reserve’s goal is to maintain the consumer price index (CPI) inflation rate at 2% per year, and the central bank will change the federal funds rate (short-term interest rates) if it strays significantly from this objective.
In 2022, the Consumer Price Index (CPI) reached its highest level in 40 years at 8%, leading to a significant push to raise interest rates by the Federal Reserve. However, as inflation has significantly decreased since then, the central bank seems likely to undo that policy.
This suggests that there is a possibility of a decrease in interest rates for the first time since March 2020. Looking at past patterns, this change could lead to a significant shift in the benchmark. S&P 500 ( ^GSPC 0.38% ) The stock market index — although the outcome may be unexpected.
The Federal Reserve may lower interest rates on three occasions by the conclusion of 2024.
In response to the economic impact of the COVID-19 pandemic, the U.S. government provided a massive amount of financial aid to the economy in 2020 and 2021. Additionally, the Federal Reserve significantly lowered interest rates to a record low range of 0% to 0.25% and infused the financial system with trillions of dollars. The process of quantitative easing involves a central bank purchasing government securities or other financial assets in order to increase the money supply and stimulate the economy. By purchasing bonds issued by the government and agencies.
An expansionary monetary policy and significant rises in the money supply typically result in… inflationary However, prices were also pushed up due to interruptions in international supply chains. Factories and shipping companies were intermittently closing down worldwide in order to contain the spread of COVID-19, resulting in scarcities of various products such as televisions and automobiles.
So, a combination of factors led to the CPI experiencing a significant increase in 2022, which led to a series of rapid rate hikes. The federal funds rate refers to the interest rate at which depository institutions lend reserve balances to other depository institutions overnight on an uncollateralized basis. Eventually stabilized between 5.25% and 5.50% following the Federal Reserve’s most recent interest rate increase in August 2023, which is significantly higher than the lowest point during the pandemic.
However, there is positive development to report as the Consumer Price Index (CPI) showed progress. By the end of 2023, the CPI stood at 4.1%, and by June 2024, it had reached a yearly rate of 3%, the latest available data. This indicates that inflation is approaching the Federal Reserve’s desired target of 2%.
Therefore, the majority of experts anticipate upcoming reductions in interest rates. CME Group According to ‘s FedWatch tool, it is anticipated that the Federal Reserve will reduce interest rates three times before the end of 2024, with one rate cut in September, another in November, and the final one in December.
Rate cuts don’t consistently have a positive impact on the stock market.
According to common belief, lowering interest rates is beneficial for the stock market as it decreases the returns on safe investments such as cash. Treasury bonds This leads investors to favor growth assets such as stocks and real estate.
Nevertheless, upon closer inspection of the chart presented below, which superimposes the federal funds rate alongside… S&P 500 Looking as far back as the year 2000, we can observe that decreasing interest rates frequently predict a drop in the stock market.
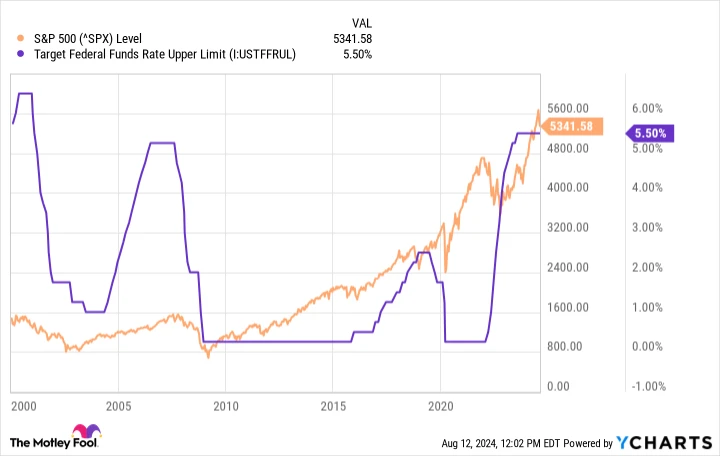
It is important to note that the overall trend for the S&P 500 is consistently positive, meaning that long-term investors should not be influenced by short-term fluctuations. possibility of upcoming decline Furthermore, there were certain dominant themes in the past that complicate this relationship. In simpler terms, we need to consider why The Federal Reserve was reducing interest rates during the time frames shown in the chart above.
- In the early 2000s, the bursting of the dot-com tech bubble led to an economic recession. The S&P 500 experienced a decline of 9.1% in 2000, 11.9% in 2001, and 22.1% in 2002.
- In the late 2000s, the worldwide economic downturn led to the Federal Reserve taking significant actions, such as quickly reducing interest rates and implementing quantitative easing (QE) measures for the first time. As a result, the S&P 500 index dropped by 37% in 2008.
- The pandemic was the main cause of the significant decrease in rates in 2020. Despite experiencing a decline of 31.8% at its lowest point, the S&P 500 managed to finish the year with positive gains due to the various stimulus measures mentioned previously.
Hence, we cannot definitively state that the stock market decreased. because The Federal Reserve lowered interest rates. However, it probably did so in response to the overall economic conditions at the time.

Credit: Getty Images.
Is there a possibility that this time will be unique or distinct?
Currently, there are no indications of an approaching crisis for the U.S. economy, or even a typical recession. some Indicators of fragility include a rise in the unemployment rate to 4.3% (up from 3.7% in January), which suggests a weakening job market that could lead to decreased consumer spending soon.
Considering that the Consumer Price Index (CPI) is close to the Federal Reserve’s desired level, it may not be suitable to continue with a tight policy approach. Also, changes in interest rates typically impact the economy with a delay, which suggests that we may not have experienced the complete consequences of the Federal Reserve’s previous rate increases.
Similarly, any reductions in interest rates at the end of this year are unlikely to impact economic indicators until around 2025. Therefore, initiating rate cuts sooner could increase the chances of preventing any avoidable decline in the U.S. economy in the future.
The stock market is influenced by the financial performance of companies, and it becomes challenging for businesses to achieve growth during an economic slowdown. Wall Street Begins to lower profit predictions, which is likely to result in a decline in stock market performance. Consequently, the S&P 500 may be decreasing concurrently with the Federal Reserve reducing interest rates.
The Federal Reserve usually lowers interest rates when it detects economic downturns, which may indicate that the S&P 500 will decline in the near future. However, immediate interest rate reductions do not necessarily mean that one should sell stocks. As previously discussed, stocks often bounce back in the long run, so any short-term decline may not be a cause for concern. This could potentially be a good time to make a purchase. .




