Social Security has been extremely important for the financial security of our aging workforce. A study conducted by the Center on Budget and Policy Priorities revealed that in 2022, 22.7 million individuals, with 16.5 million being seniors aged 65 and above, were brought out of poverty due to their Social Security benefits.
Additionally, data from Gallup’s annual surveys over the past twenty years indicate that as many as 90% of retired individuals rely on their monthly pension to help with a portion of their costs. In simpler terms, Social Security is a government program that provides financial assistance to individuals who are retired, disabled, or survivors of deceased workers. is a program that the majority of retired individuals and older Americans would find it difficult to manage without.

Picture credit: Getty Images.
While Social Security is in no risk of facing financial collapse, insolvency, or extinction The program’s basis is displaying indications of deterioration, which has endangered the future payout projections.
Contents
- 1 The Social Security program is projected to have a funding gap of more than $23 trillion over the long term.
- 2 Can you manage a decrease of $508 per month in your Social Security payment?
- 3 What caused the collapse of Social Security’s previously strong base?
- 4 Legislators acknowledge that there is an issue, but there is no easy fix.
The Social Security program is projected to have a funding gap of more than $23 trillion over the long term.
Since the initiation of Social Security payments to retired workers in 1940, the Social Security Board of Trustees has been annually publishing a report that provides a detailed analysis of the program’s financial status. This report not only examines the current financial situation but also predicts the effects of policy adjustments, population changes, and other variables on revenue generation and benefit payments over a period of 10 years (short term) and 75 years (long term) after its publication.
Starting from 1985, each Trustees Report has consistently warned that the revenue generated in the long run would not be enough to meet the expenses. In simpler terms, the signs have indicated for a while now that Social Security is dealing with a deficit in funding for a 75-year period.
According to the 2024 Trustees Report, Social Security is projected to have a significant funding shortfall of $23.2 trillion until 2098. This deficit has been consistently increasing in size over the past few years.
However, there is a more significant concern than the potential appearance of Social Security in 2098.
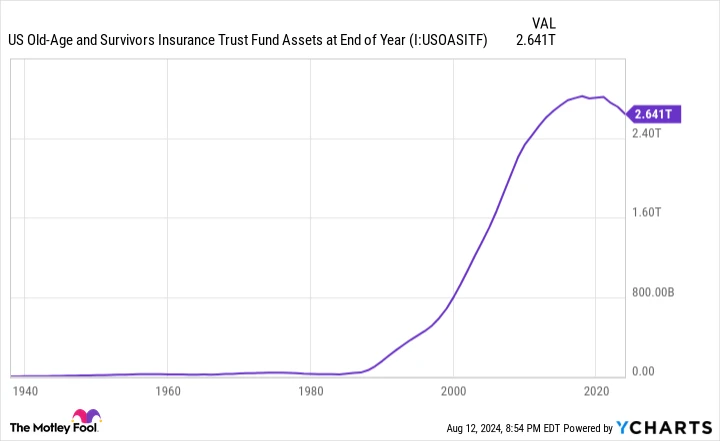
The OASI’s financial reserves may run out in nine years. The assets of the US Old-Age and Survivors Insurance Trust Fund at the end of the year. data by YCharts .
Can you manage a decrease of $508 per month in your Social Security payment?
Based on the most recent Trustees Report, the Old-Age and Survivors Insurance Trust Fund (OASI) is expected to deplete its savings by 2033. This fund is in charge of distributing benefits to over 51 million retired workers and 5.8 million survivor beneficiaries. Asset reserves “reflect the surplus funds accumulated since the start of the program, which are then invested in government bonds that earn interest.”
In summary, the decrease in the OASI’s asset reserves does not indicate that it would go bankrupt or become insolvent. Instead, it would indicate that the current payment plan, which includes yearly cost-of-living increases, is affected. COLAs It is not feasible in the long run.
The Trustees anticipate that By 2033, significant reductions in benefits of as much as 21% may be required. to maintain payments until 2098 without requiring any additional cuts.
By June 2024, the typical retired worker receiving benefits was getting $1,918.28 each month. Looking ahead to 2033, with an estimated 2.6% increase in benefits each year (based on the average over the last 20 years), the average monthly benefit for retired workers would be around $2,416.79. However, if there is a 21% cut in OASI benefits in nine years, the monthly payment would decrease by $507.53, resulting in an annual reduction of approximately $6,090.
What caused the collapse of Social Security’s previously strong base?
Given that the primary retirement program in the United States experienced over 30 years (1984-2017) of annual growth in its asset reserves, many individuals who currently receive or will receive benefits in the future are questioning how its previously strong foundation started to weaken.
I can guarantee you that it is completely unrelated to popular misconceptions about social media. The Congress is misappropriating funds. “Undocumented workers benefiting from the system” is another false claim. The increasing funding gap in Social Security is actually due to various demographic changes that are currently taking place.
For instance, the Social Security system depends on a significant influx of legal immigrants coming into the United States annually. Immigrants are generally younger, so they are likely to work for many years and pay into the program through the 12.4% payroll tax before eventually receiving retirement benefits themselves. The rate of net migration to the United States has decreased annually since 1998. , using information from the United Nations.
Yet another issue that cannot be denied is the fact that The fertility rate in the United States reached a record low in 2023. Due to various factors such as postponing marriage and economic uncertainties in the U.S., there is a decline in the number of children being born. This trend will lead to a decreased worker-to-beneficiary ratio in the future.
Income inequality is also deteriorating. In 2024, Social Security’s payroll tax applies to all earned income (excluding investment income) between $0.01 and $168,600, while income above $168,600 is not subject to this tax. The proportion of earned income exempted from payroll taxes has notably risen over the past forty years.

Photo credit: Getty Images.
Legislators acknowledge that there is an issue, but there is no easy fix.
The only way to prevent significant reductions in benefits is for our elected officials on Capitol Hill to take action. While politicians from both parties acknowledge that there are issues with the country’s main retirement program, they are working to find solutions from different perspectives.
While you can Examine the policy suggestions of both parties more thoroughly. In essence, the main point is this:
- A majority of Democrats in Congress support raising taxes on wealthy individuals and enhancing benefits for individuals with low lifetime earnings.
- The majority of Republicans in Congress favor increasing the. the age at which a person can receive full retirement benefits from Social Security to decrease program expenditures for the next generations.
Both comprehensive proposals would enhance Social Security, yet they each have distinct drawbacks.
Increasing the age at which individuals can receive full retirement benefits would lead to lower total benefit payments over their lifetime. This would require future retirees to either delay receiving their full benefits or accept a lower amount if they claim them early. They would not take any action to address the anticipated depletion of the OASI’s asset reserves. Within a span of only nine years.
Raising taxes on wealthy individuals could potentially bring in more money and delay the depletion of the asset reserve of the OASI for several years or even decades, depending on how the extra funds are used. fails to even come close to addressing the $23.2 trillion deficit in long-term funding .
Due to the lack of agreement between Democrat and Republican legislators, and the necessity of bipartisan collaboration to make changes to the Social Security Act in the Senate (requiring 60 votes), there is no straightforward solution to this escalating issue.




